MybatisPlus学习笔记
1. 快速入门
实现步骤:
1.1 引入依赖
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
|
1.2 定义Mapper
- MybatisPlus提供了一个基础的BaseMapper接口
- 修改mp-demo中的com.itheima.mp.mapper包下的UserMapper接口,让其继承BaseMapper:
1
2
| public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
}
|
2. 常见注解
2.1 默认情况
MybatisPlus就是根据PO实体的信息来推断出表的信息,从而生成SQL的。默认情况下:
- MybatisPlus会把PO实体的类名驼峰转下划线作为表名
- MybatisPlus会把PO实体的所有变量名驼峰转下划线作为表的字段名,并根据变量类型推断字段类型
- MybatisPlus会把名为id的字段作为主键
2.2 @TableName
- 描述:表名注解,标识实体类对应的表
- 使用位置:实体类
2.3 @TableId
- 描述:主键注解,标识实体类中的主键字段
- 使用位置:实体类的主键字段
IdType属性的常见值:
- AUTO:利用数据库的id自增长
- INPUT:手动生成id
- ASSIGN_ID:雪花算法生成Long类型的全局唯一id,这是默认的ID策略
2.4 @TableField
普通字段注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| @TableName("user")
public class User {
@TableId
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
@TableField(is_married")
private Boolean isMarried;
@TableField("`concat`")
private String concat;
}
|
添加@TableField注解的一些特殊情况:
- 成员变量名与数据库字段名不一致
- 成员变量是以isXXX命名,按照JavaBean的规范,MybatisPlus识别字段时会把is去除,这就导致与数据库不符。
- 成员变量名与数据库一致,但是与数据库的关键字冲突。使用@TableField注解给字段名添加转义字符:``
3. 核心功能
3.1 条件构造器
除了新增以外,修改、删除、查询的SQL语句都需要指定where条件。因此BaseMapper中提供的相关方法除了以id作为where条件以外,还支持更加复杂的where条件。
Wrapper就是条件构造的抽象类
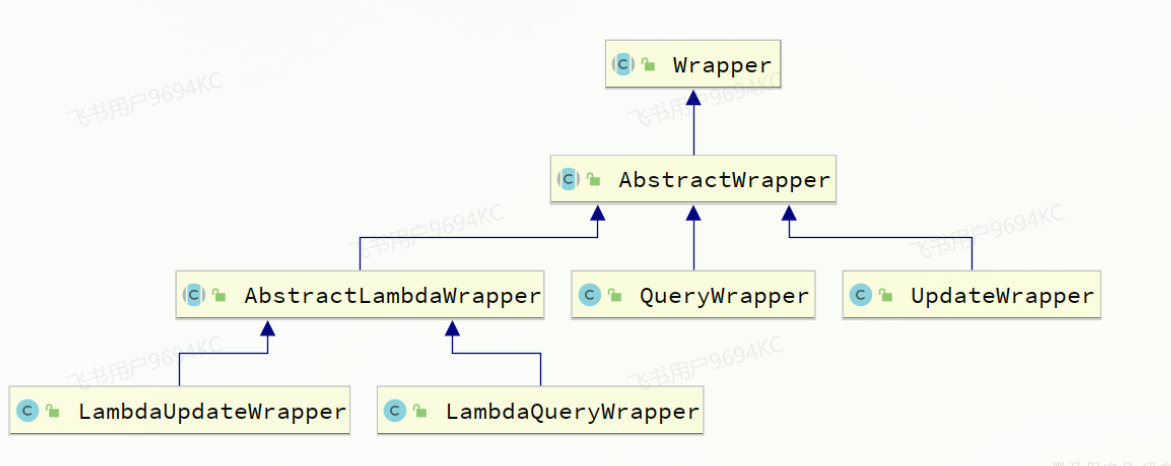
3.1.1 QueryWrapper
查询:查询出名字中带o的,存款大于等于1000元的人。代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| @Test
void testQueryWrapper() {
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<User>()
.select("id", "username", "info", "balance")
.like("username", "o")
.ge("balance", 1000);
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(wrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
|
3.1.2 UpdateWrapper
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| @Test
void testUpdateWrapper() {
List<Long> ids = List.of(1L, 2L, 4L);
UpdateWrapper<User> wrapper = new UpdateWrapper<User>()
.setSql("balance = balance - 200")
.in("id", ids);
userMapper.update(null, wrapper);
}
|
3.1.3 LambdaQueryWrapper
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| @Test
void testLambdaQueryWrapper() {
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.lambda()
.select(User::getId, User::getUsername, User::getInfo, User::getBalance)
.like(User::getUsername, "o")
.ge(User::getBalance, 1000);
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(wrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
|
3.2 自定义SQL
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| @Test
void testCustomWrapper() {
List<Long> ids = List.of(1L, 2L, 4L);
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<User>().in("id", ids);
userMapper.deductBalanceByIds(200, wrapper);
}
|
然后在UserMapper中自定义SQL:
1
2
3
4
| public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
@Select("UPDATE user SET balance = balance - #{money} ${ew.customSqlSegment}")
void deductBalanceByIds(@Param("money") int money, @Param("ew") QueryWrapper<User> wrapper);
}
|
3.3 Service接口
3.3.1 介绍
MybatisPlus不仅提供了BaseMapper,还提供了通用的Service接口及默认实现,封装了一些常用的service模板方法。
通用接口为IService,默认实现为ServiceImpl,其中封装的方法可以分为以下几类:
- save:新增
- remove:删除
- update:更新
- get:查询单个结果
- list:查询集合结果
- count:计数
- page:分页查询
3.3.2 基本用法
自定义Service接口继承IService以拓展方法。同时,让自定义的Service实现类继承ServiceImpl
1
2
3
| public interface IUserService extends IService<User> {
}
|
编写UserServiceImpl类,继承ServiceImpl,实现UserService
1
2
3
| @Service
public class UserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<UserMapper, User> implements IUserService {
}
|
3.3.3 Lambda
IService中还提供了Lambda功能来简化我们的复杂查询及更新功能
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| @Override
@Transactional
public void deductBalance(Long id, Integer money) {
User user = getById(id);
if (user == null || user.getStatus() == 2) {
throw new RuntimeException("用户状态异常!");
}
if (user.getBalance() < money) {
throw new RuntimeException("用户余额不足!");
}
int remainBalance = user.getBalance() - money;
lambdaUpdate()
.set(User::getBalance, remainBalance)
.set(remainBalance == 0, User::getStatus, 2)
.eq(User::getId, id)
.eq(User::getBalance, user.getBalance())
.update();
}
|
4. 扩展功能
4.1 代码生成
使用MybatisX插件即可
SpringBoot中MybatisX插件的简单使用教程(超详细!!)
4.2 静态工具
有的时候Service之间也会相互调用,为了避免出现循环依赖问题,MybatisPlus提供一个静态工具类:Db,其中的一些静态方法与IService中方法签名基本一致
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| @Override
public UserVO queryUserAndAddressById(Long userId) {
User user = getById(userId);
if (user == null) {
return null;
}
List<Address> addresses = Db.lambdaQuery(Address.class)
.eq(Address::getUserId, userId)
.list();
UserVO userVO = BeanUtil.copyProperties(user, UserVO.class);
userVO.setAddresses(BeanUtil.copyToList(addresses, AddressVO.class));
return userVO;
}
|
在查询地址时,我们采用了Db的静态方法,因此避免了注入AddressService,减少了循环依赖的风险。
4.3 逻辑删除
对于一些比较重要的数据,我们不删除数据库中的数据,而是
- 在表中添加一个字段标记数据是否被删除
- 当删除数据时把标记置为true
我们要在application.yml中配置逻辑删除字段
1
2
3
4
5
6
| mybatis-plus:
global-config:
db-config:
logic-delete-field: deleted
logic-delete-value: 1
logic-not-delete-value: 0
|
4.4 枚举处理器
MybatisPlus提供了一个处理枚举的类型转换器,可以帮我们把枚举类型与数据库类型自动转换
4.4.1 定义枚举
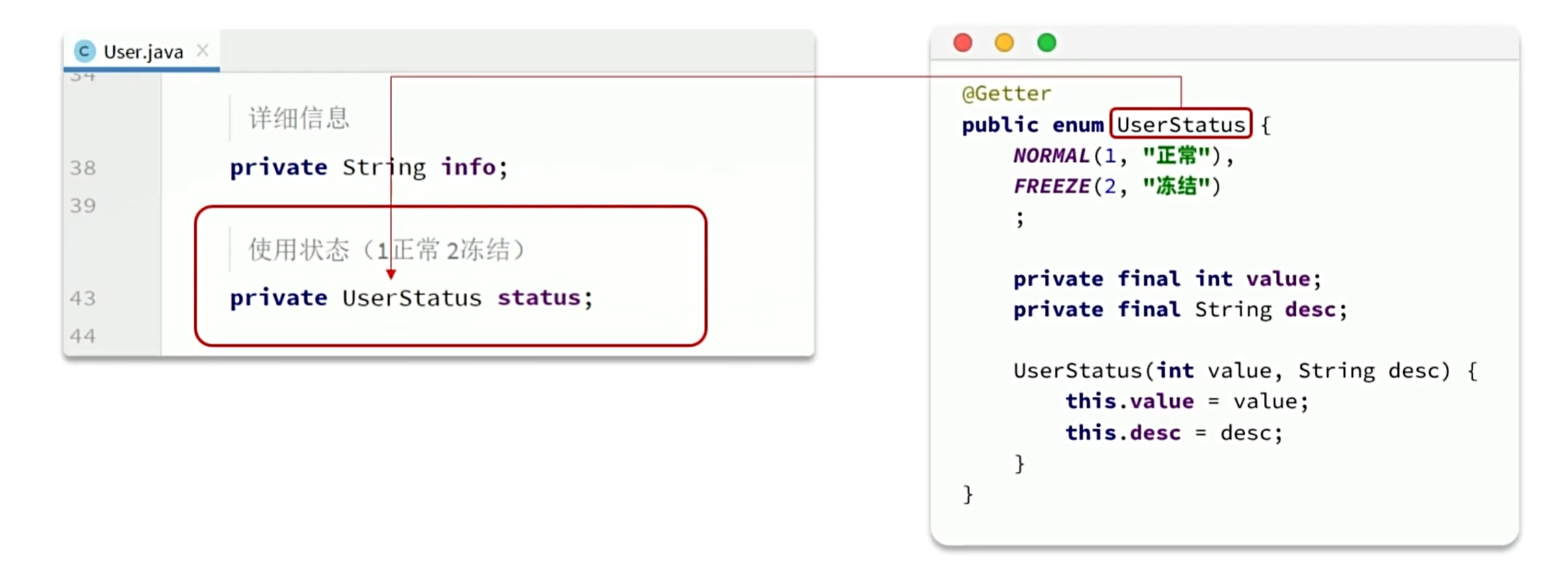
4.4.2 @EnumValue
MybatisPlus提供了@EnumValue注解来标记枚举属性
1
2
| @EnumValue
private final int value;
|
表示value字段的值是数据库值
4.4.3 配置枚举处理器
在application.yaml文件中添加配置
1
2
3
| mybatis-plus:
configuration:
default-enum-type-handler: com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.handlers.MybatisEnumTypeHandler
|
4.5 JSON类型处理器
数据库的user表中有一个info字段,是JSON类型。而目前User实体类中却是String类型。处理JSON就可以使用JacksonTypeHandler处理器
使用类型处理器
将User类的info字段修改为UserInfo类型,并声明类型处理器:
1
2
| @TableField(typeHandler = JacksonTypeHandler.class)
private UserInfo info;
|
5. 插件功能(以分页插件为例)
MybatisPlus提供了很多的插件功能,进一步拓展其功能。
- PaginationInnerInterceptor:自动分页
- TenantLineInnerInterceptor:多租户
- DynamicTableNameInnerInterceptor:动态表名
- OptimisticLockerInnerInterceptor:乐观锁
- IllegalSQLInnerInterceptor:sql 性能规范
- BlockAttackInnerInterceptor:防止全表更新与删除
5.1 配置分页插件
在项目中新建一个配置类:MybatisConfig.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.DbType;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.MybatisPlusInterceptor;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.inner.PaginationInnerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class MybatisConfig {
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor() {
MybatisPlusInterceptor interceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new PaginationInnerInterceptor(DbType.MYSQL));
return interceptor;
}
}
|
5.2 分页查询的测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| @Test
void testPageQuery() {
Page<User> p = userService.page(new Page<>(2, 2));
System.out.println("total = " + p.getTotal());
System.out.println("pages = " + p.getPages());
List<User> records = p.getRecords();
records.forEach(System.out::println);
}
|
END

